
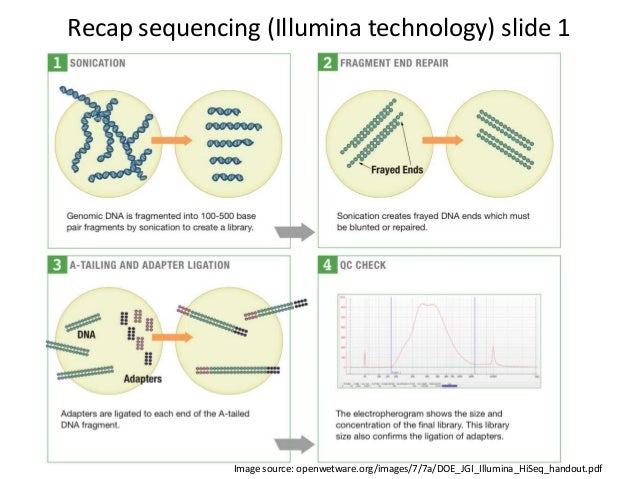
These workflows cover all the analytical steps required for NGS data, from processing the raw reads to variant calling and annotation. The GPCG implements flexible workflows for basic sequence alignment, sequence data quality control, single nucleotide polymorphism analysis, copy number variant identification, annotation, and visualization of results. We describe our method, the Graphical Pipeline for Computational Genomics (GPCG), to perform the computational steps required to analyze NGS data.
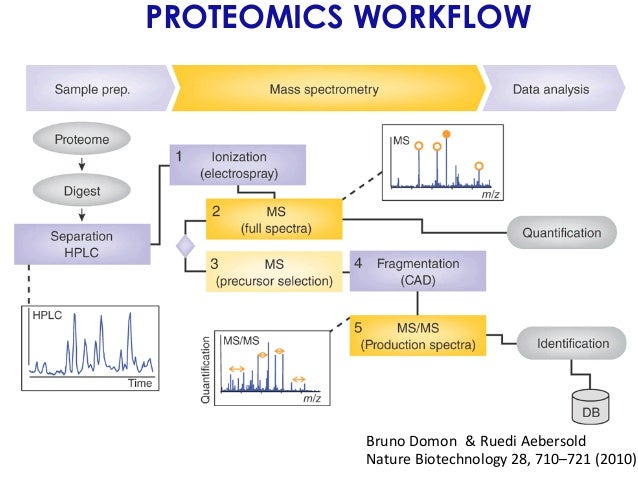
We review the existing methods for processing NGS data, to place into context the rationale for the design of a computational resource. The huge analytical burden of data from genome sequencing might be seen as a bottleneck slowing the publication of NGS papers at this time, especially in psychiatric genetics.

These achievements have been made possible by next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, which require substantial bioinformatics resources to analyze the dense and complex sequence data. These methods can be applied to complex disorders as well, and have been adopted as one of the current mainstream approaches in population genetics. Whole-genome and exome sequencing have already proven to be essential and powerful methods to identify genes responsible for simple Mendelian inherited disorders.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
